Welcome back –
Here is a post from Dr Mercola’s site that I think everyone who loves bread should read.
I’ll be back next week with more of my own research & findings….
Simple Way to Shed Pounds and Decrease Tiredness – Stop Eating This
Posted By Dr. Mercola | June 30 2011 | 31,338 views | Disponible en Español
In 1911, the bread which made up 40 percent of the diet of the impoverished people of Britain was blamed for widespread poor health. Modern nutritional science confirms the accuracy of this assessment.
Refined white flour contains almost no natural minerals and vitamins. In particular, vitamin B deficiency from poor diet resulted in a range of illnesses that the Victorians called ‘wasting diseases’. And white flour at the time was usually laced with alum, which made bad flour look whiter.
According to the Daily Mail:
“[In modern times], the Real Bread Campaign, a non-profit pressure group, claims that bread has actually gotten worse since 1911 in terms of secret adulterants — enzymes that do not have to be declared on labels — still being smuggled into it. Today, despite the modern fashion for healthy eating, ‘nutritionally empty’ white bread accounts for more than 50 percent of what we buy.”
Sources:
The Daily Mail June 15, 2011
It’s truly astounding—100 years ago, low-quality bread made up about 40 percent of the average Briton’s diet (and the situation was likely similar in the US as well), and today, even lower quality bread makes up nearly 50 percent of the average diet!
Back in 1911, white bread was identified as a primary culprit for the declining health of the British population, which led to a massive campaign to revert back to more wholesome bread. At the time, wholegrain bread was considered a sign of poverty, so people from all levels of society sought after white, refined flour bread.
The campaign spearheaded by The Daily Mail was eventually successful. But it didn’t last long… White bread was actually banned during World War II in the UK, and as a result, Britons were said to be in better health by 1947 after subsisting on limited rations of wholegrain breads for eight years.
However, at the end of the war, white bread was rendered legal once again, and today, more than 60 years later, our grocery shelves are stocked with breads and grain-products that are of even lower quality than 100 years ago… And, as in 1911, white processed bread is a major contributor to rampant obesity and poor health.
Do You Know the Chemicals Lurking in Your Bread?
As illustrated in The Daily Mail, the quality of bread has gotten far worse rather than better over the years. Back in 1911, salt, cheap fats, alum, lime powder, and bleaching constituted “bad” bread. Today, there’s a whole new breed of health-harming ingredients to contend with in your typical store-bought bread, including:
Many of these ingredients are hidden, as they’re not required to be listed on the label. I’ve written numerous articles on many of these ingredients. For more information, simply follow the links provided. But hidden and potentially harmful ingredients aren’t the only problem with modern bread. Today we have such things as Wonder Bread, and it’s a wonder that anyone even considers it to be “bread” in the first place…
Refined Foods are Devoid of Nutrients
It’s important to realize that when food is refined, vital nutrients are destroyed. In some cases it’s questionable whether what remains is even fit to be considered food… at least if the term “food” implies something of nutritional value. In terms of bread, once you remove the most nutritious part of the grain, it essentially becomes a form of sugar.
Consider what gets lost in the refining process:
| Half of the beneficial unsaturated fatty acids |
50 percent of the calcium |
80 percent of the iron |
50-80 percent of the B vitamins |
| Virtually all of the vitamin E |
70 percent of the phosphorus |
98 percent of the magnesium |
And many more nutrients are destroyed — simply too many to list. |
How Processed Grains Can Deteriorate Your Health
The end result of the excessive consumption of white bread and other processed forms of grain products can be seen all around you in the form of:
Vitamin B deficiencies in particular contribute to a wide range of illnesses, and vitamin B deficiencies are pervasive around the world. For example, an estimated 25 percent of American adults are deficient in B12.
We’ve also seen an extraordinary rise in digestive illnesses, such as gluten intolerance and Celiac disease, and modern industrial baking methods are likely a major contributor to these widespread problems. The rise in asthma and allergies may also be related to our modern food processing and manufacturing practices. For example, one of the enzymes commonly used in modern bread making is amylase, which is known to cause asthma.
Many also forget that most commercial wheat production is, unfortunately, a “study in pesticide application,” beginning with the seeds being treated with fungicide. Once they become wheat, they are sprayed with hormones and pesticides. Even the bins in which the harvested wheat is stored have been coated with insecticides. These chemicals all contribute to increasing the average person’s toxic load, which is a contributing factor to virtually every possible disease imaginable. I can’t think of any illness that is not made worse by frequent toxic exposure, such as what we get through conventionally-grown foods and unfiltered water.
Whereas old time mills ground flour slowly, today’s mills are designed for mass-production, using high-temperature, high-speed steel rollers. Next, it’s hit with another chemical insult–a chlorine gas bath (chlorine oxide). This serves as a whitener, as well as an “aging” agent. Flour used to be aged with time, improving the gluten and thus improving the baking quality. Treating it with chlorine instantly produces similar qualities in the flour (with a disturbing lack of concern about adding another dose of chemicals to your food).
The resulting white flour is nearly all starch, and now contains a small fraction of the nutrients of the original grain. Additionally, the chemical treatments on the grain results in the formation of a byproduct, alloxan—a poison used in the medical research industry to induce diabetes in healthy mice. Alloxan causes diabetes by spinning up enormous amounts of free radicals in pancreatic beta cells, thus destroying them. Beta cells are the primary cell type in areas of your pancreas called islets of Langerhans, and they produce insulin; so if those are destroyed, you develop diabetes.
Given the raging epidemic of diabetes and other chronic diseases in this country, it may be unwise to be complacent about a toxin such as this in your bread, even if it is present in small amounts…
Why a High-Carb Diet Can be Disastrous to Your Health
Overconsumption of carbs is the primary driving factor for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Unfortunately, the dietary establishment has unwisely been extolling the virtues of carbohydrates while warning you to avoid fats. But anyone who bought into the high-carb, low-fat dietary recommendations has likely struggled with their weight and health, wondering what they’re doing wrong…
The truth of the matter is that a diet high in grain carbs (as opposed to vegetables) and low in fat may be dangerous to your health, and if you want to shed excess weight and improve your health, the converse diet is what you’re looking for!
Why are high-carb diets so bad?
In a nutshell, overeating carbohydrate foods can prevent a higher percentage of fats from being used for energy, and lead to an increase in fat storage. It also raises your insulin levels, which in short order can cause insulin resistance, followed by diabetes. Insulin resistance is also at the heart of virtually every disease known to man.
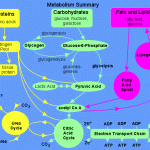
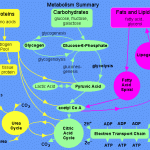
Contrary to popular belief, eating fat does NOT make you fat—carbohydrates, such as sugar and grains, do. Your body has a limited capacity to store excess carbohydrates, but it can easily convert those excess carbohydrates into excess body fat. Any carbohydrates not immediately used by your body are stored in the form of glycogen (a long string of glucose molecules linked together). Your body has two storage sites for glycogen: your liver and your muscles. Once the glycogen levels are filled in both your liver and muscles, excess carbohydrates are converted into fat and stored in your adipose, that is, fatty, tissue.
So, although carbohydrates are fat-free, excess carbohydrates end up as excess fat.
But that’s not the worst of it. Any meal or snack high in carbohydrates will also generate a rapid rise in blood glucose. To adjust for this rapid rise, your pancreas secretes insulin into your bloodstream, which then lowers the levels of blood glucose. The problem is that insulin is essentially a storage hormone, evolved to put aside excess carbohydrate calories in the form of fat in case of future famine. So the insulin that’s stimulated by excess carbohydrates aggressively promotes the accumulation of body fat!
Too Much Wheat or Grain Converts Into Fat
In other words, when you eat too much bread, pasta, and any other grain products, you’re essentially sending a hormonal message, via insulin, to your body that says “store fat.”
Additionally, increased insulin levels also:
- Make it virtually impossible for you to use your own stored body fat for energy
- Suppress two important hormones: glucagon and growth hormone. Glucagon promotes the burning of fat and sugar. Growth hormone is used for muscle development and building new muscle mass.
- Increases hunger: As blood sugar increases following a carbohydrate meal, insulin rises with the eventual result of lower blood sugar. This results in hunger, often only a couple of hours (or less) after the meal.
So, all in all, the excess carbohydrates in your diet not only make you fat, they make sure you stay fat. Cravings, usually for sweets, are frequently part of this cycle, leading you to resort to snacking, often on more carbohydrates. Not eating can make you feel ravenous shaky, moody and ready to “crash.” If the problem is chronic, you never get rid of that extra stored fat, and your energy and overall health is adversely affected.
Below is a list of some of the most common complaints of people with insulin resistance (IR). Many of these symptoms may occur immediately following a meal of carbohydrates; others may be chronic:
| Fatigue. Some are tired just in the morning or afternoon; others are exhausted all day. |
Brain fogginess. The inability to concentrate is the most evident symptom. Loss of creativity, poor memory, failing or poor grades in school often accompany insulin resistance, as do various forms of “learning disabilities.” |
Hypoglycemia. Feeling jittery, agitated and moody is common in IR, with an almost immediate relief once food is eaten. Dizziness is also common, as is the craving for sweets, chocolate or caffeine. |
| Intestinal bloating. Most intestinal gas is produced from dietary carbohydrates. Sometimes the intestinal distress can become quite severe, resulting in a diagnosis of “colitis” or “ileitis.” |
Sleepiness. Many people with IR get sleepy immediately after meals containing more than 20-30 percent carbohydrates. This is typically a pasta meal, or even a meat meal that includes bread or potatoes and a sweet dessert. |
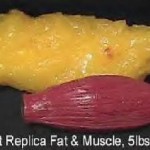
Increased fat storage and weight. In many people, the most evident sign is a large abdomen, or belly fat. |
| Increased triglycerides. High triglycerides in the blood are often seen in overweight persons. But even those who are not too fat may have stores of fat in their arteries as a result of IR. These triglycerides are the direct result of carbohydrates from the diet being converted by insulin. |
Increased blood pressure. It is well known that most people with hypertension have too much insulin and are IR. It is often possible to show a direct relationship between the level of insulin and the level of blood pressure: as insulin levels elevate, so does blood pressure. |
Depression. Carbohydrates are a natural “downer,” and it’s not uncommon to see many depressed persons also having IR. Carbohydrates do this by changing your brain chemistry—they increase serotonin, which produces a depressing or sleepy feeling. (This is a significant consideration for those trying to learn, whether at school, home or work.) |
Does this sound like you?
One of the Fastest Ways to Dramatically Improve Your Health
The best suggestion for anyone wanting to shed excess fat and improve health is to moderate and normalize your insulin response by limiting (ideally, eliminating) your intake of refined sugars and fructose, and limiting all other carbohydrate intake as much as possible. (Proteins and fats generally do not produce much insulin.)
With the stress of insulin resistance eliminated, your body can finally be able to correct many of its own problems, and this is also why I keep reminding you that the underlying factor of most disease states that MUST be addressed is insulin resistance. Once you’ve normalized your insulin levels, your body actually has a phenomenal capacity for self-healing.
<script type=”text/javascript” src=”http://www.mercola.com/js/citation.js” language=”javascript”></script>