Welcome back –
There have been millions of words written and many millions more I’m sure to come all on the subject of how to lose weight and build muscle. Now regular readers know that I hate the term ’lose weight’ it is inaccurate & wrong – your goal is to lose body fat. It is entirely possible to lose kilos of fat but have the scales drop by less than that amount because you’ve added some muscle.
So losing weight is out, losing fat is in.
The questions usually revolve around two polar opposites – either how do you eat to add muscle without adding fat, or how to diet to lose fat whilst still adding muscle.
Do use intermittent fasting? Atkins? Palm Beach? Drink Shakes 3 x a day? Run miles every day? Work out twice a day? Eat low carb? Eat high carb? Add the latest magic food?
You know there are plenty of available strategies to consider and they all try to address one or both of the needs mentioned above but results are mixed. What works for some fails for others. The unpalatable truth is that there is no magic one-size fits every metabolism solution available. The cookie cutter approach needs to stay in the kitchen with the pastry.

For Fat Loss there isn't a cookie cutter approach...
There is a common thread in all of the effective strategies though – they utilise your metabolism to work with you for the desired results and they all – the ALL – harness the power of insulin.
Insulin has been given a bad rap in the popular press – it does not cause obesity, it is not the ‘fat hormone’. It is true because it is a ‘carrier’ hormone insulin has the ability to induce fat storage if the environment allows for this.
However id allowed to work as it is supposed insulin is in fact the single most anabolic hormone present in your body (remember anabolic means build, catabolic is to tear down)
Insulin ensures that your cells are ‘fed’, that amino acids are taken up and protein synthesis is completed.
Energy cannot be destroyed, just transformed.
If I remember my High School science correctly we were taught that energy can be changed from one form to another (ie transformed) but it can’t be created or destroyed.
To lose body fat you need to use up more energy than you take in. To lose a pound you need to either take in an amount equal to; or use up a total of 3500 calories. To gain weight (I deliberately did not say fat in this case – to build serious muscle you have to eat a lot of nutrient dense foods. Google Chris Hemsworth’s diet for his muscle gain for Thor) you have to ingest more calories than you need to remain in energy homeostasis if you are going to support lean tissue gains.

Serious training needs serious eating to support serious growth...
Of course if you eat more than you need and you are not exercising to create lean body mass then you’ll get fat. The Bottom line is that if you eat too much, without the mitigating effects of high intensity exercise, you’ll get fat, no matter where the calories are coming from.
In the real world, the world without chemical interdiction of the body’s processes, there is simply no mystical combination of nutrients – macro, micro or otherwise – of meal timing of super supplements etc et that can change this fact. It simply is – eat more than your body needs on a consistent basis and you’ll get fatter.
BUT – we know that a calorie is NOT just a calorie and all calories are NOT created equal. Different macro- & micronutrients produce different long-term effects hormonally and metabolically.
This brings us to nutrient partitioning.
Nutrient Partitioning: Macronutrients Matter
Nutrient partitioning is another of those scientific sounding terms that a lot of folk use to make their theories for weight loss (not fat ahem…) sound more solid. Dr Scott Connelly the man who with Bill Phillips ‘created’ MetRX, was the first to use the term I supplement marketing. Now a lot of folk do.
This doesn’t mean it doesn’t exist, or that it’s not rooted in solid science it is. Nutrient partitioning is regulated by a co-ordinated, multi-part symphony that consists of liver & gut action, brain & Central Nervous System (CNS), of muscle & fat tissues, of hormones & ion channels and more besides. Even now we are still not entirely sure of all of the components and exactly how nutrient partitioning works…But work it does.

The supplement that introduced the term 'Nutrient partitioning' into marketing speak...
More importantly we can make it work for us.
What is done with the food we eat by our bodies is a function of nutrient partitioning.
The calories we ingest are either burned for fuel, used for repair & growth or stored as energy for future use (yep – glycogen first then fat once the glycogen stores are full).
Naturally we’d want as much of the food we eat to be used as fuel for repair and lean tissue growth with as little as possible being stored as fat. Whether we are a week end athlete, a couch potato or a real athlete we all agree on one thing we want to eat our food with the absolute minimum stored as bodyfat.
So whilst you can’t destroy the energy we gain from food the macronutrients we ingest do matter and have an effect on nutrient partitioning. The question is how do we maximise the glycogen stores in our muscles & liver and minimise our fat stores whilst conditioning our metabolism to either maintain or gain lean muscular tissue?
Part of the answers lies in the fact that nutrient partitioning becomes less efficient, less effective the more insulin resistant that you become. In diabetics and the obsese nutrient partitioning is so out of shape that it becomes dysfunctional.
Insulin is enormously important in the actions of nutrient partitioning – the more insulin sensitive you are the better it works, the more that nutrients are partitioned & used by your body towards our muscle building, low fat storing goals. The more insulin resistant – the more fat you store as Nutrient partitioning twists out of true.
Insulin: Sensitive = Good, Resistant = Bad
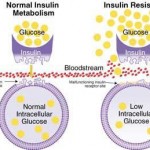
You keep a knockin' but you can't come in - Insulin Resistance
We eat food and the carbs are broken down to glucose and absorbed by our blood stream. This gives our bodies an immediate and easy to access source of fuel. If the fuel is required it is burnt (via ATP synthesis) if not needed it is stored – both of these actions are controlled by Insulin.
Under insulin’s direction glucose is either stored as glycogen in the liver and muscle tissues, or it is converted to triglycerides and stored as body fat. That’s it, only 2 possibly outcomes.
Despite what we have read, and the fact that we want to max out glycogen storage and restrict fat storage – Insulin doesn’t care. Its action is constant – it gets out fat cells to be always taking up glucose. Once in the fat cell the glucose is transformed to fatty acids or glycerol both of which are needed to make up triglycerides. Which then get stored as fat.
So what?! you say – well this means that our bodies are ALWAYS storing fat after each & every meal. It sounds scarier than it is really is though…
The amount of fat stored under normal circumstances is under 15% because the lion’s share of the glucose (85 – 95%) is taken up & used by the muscles and as a part of body repair actions.
The key here is ‘under normal circumstances’…
Eat too many nutrient sparse, processed carbs and the whole glucose as our nutrient partitioning friend scenario alters radically. Too much available glucose means that the glycogen stores quickly fill up (their storage is limited) and the excess glucose is turned to fatty acids and then stored as triglycerides – you add fat. Speed is an issue here as well glycogen stores rapidly fill as they are the primary source of energy for our muscles and major organs like the liver. These stores can empty at a slower rate than they fill (although it is still quite quickly) even if we are out under sudden wide ranging stress, hit a hard exercise session etc. This emptying requires that more glucose be taken up to place what is used. Thing is if there is an excess of glucose in the blood stream and the just filled glycogen stores are not given a chance to empty then we

They don't come much more processed than this...
store it as fat.
Too much glucose in our blood stream is, ironically, poisonous – this is why insulin’s main purpose is to clear it from the blood through glycogen and / or fat storage. Our bodies are designed to constantly clear glucose from our blood streams. It does this by using insulin to interact with a specific receptor on fat cells that signals the fat cell to uptake the surplus glucose. This signal is sent once the glycogen stores are full.
Thing is – Insulin is just the messenger, the uptake of the glucose is controlled by a receptor. If your body has become insulin resistant the receptor ignores the insulin. But the glucose remains toxic so more insulin is released in quantities that force the receptors to allow the glucose & other nutrients to get into the cells.
Gain so what?! You say – well thing is a non-virtuous circle of feedback is created – the more insulin used to ‘pry’ open the cell receptors the more resistant to the actions of insulin they become so the more insulin is released…Even worse the insulin resistance in muscle & other tissues also rises meaning that the insulin sensitivity has decreased.
Normally this happens in these tissues when the glycogen stores are full, but with increased resistance mimicking the ‘full’ signal glycogen stores may not fully fill up falsely creating an excess of glucose in the blood stream which causes the dreaded insulin spike to get it cleared. Not only does insulin resistance cause you to get fat but it also robs your lean tissues and organs of a full complement of energy.
Consistently increased insulin levels also cause the metabolism to become “stuck” in its carbohydrate-burning mode. It does this by inhibiting the fat burning genes and by activating the carb metabolism ones. So your body develops a preference for carbs as all fuel and fat as little or none.
So we need to restore or at least improve our insulin sensitivity.
How to go about Improving Insulin Sensitivity

Good Carbs
Realise as a start that carbs are not bad, they’re not the enemy. Excess carbs, especially from highly processed nutrient sparse sources are.
Firstly watch what types of carbs you are eating. Again – you know the drill eat carbs from sources as unprocessed and as nutrient dense as possible. Next look at when you are eating you carbs. Aim to have about 30% of your daily intake at breakfast with a godly amount of lean protein.
Spread the other 70% over the day – again being aware of the source of them. If you are working out ensure that you have a decent ‘hit’ of carbs with protein in the hour after working out.
Look everyone’s metabolism and its needs are different – these are only rules of thumb – you have to see what works best for you. Main thing is to eat fibrous, unprocessed carbs mainly from fruit & vegetables and sparingly from grains. Eating this way will bolster your chances of nutrient partitioning working more for and less against you.
Remember that most folk have about 100 grams of glycogen in their liver and another 400-odd in their muscles. If you were to totally deplete these stores any amount of carbs over 500 grams not burned immediately for energy would be destined for fat storage.
So again try to limit your carb intake to avoid taking in an excessively high amount. Also again – check your sources of carbs – lean towards the fibrous, the unprocessed as much as possible.
What we really need is a way to improve our nutrient partition by increasing our insulin sensitivity, or by decreasing our insulin resistance.
Improving nutrient partitioning by combating insulin resistance
I have written before about the effect of whole body inflammation on metabolism, fat storage and heart disease. It should come as no surprise that by reducing any inflammation in the body we also improve our insulin sensitivity.

Look for oils that have a low Omega 6 and a high Omega 3 porofile
Leaving aside the cogent arguments of the Paleo folk regarding the inflammatory effects of grains, we know that a major cause of inflammation is the imbalance between Omega 3 & 6’s. Turns out that this imbalance is also a supporting factor for insulin resistance. High Omega 6’s means a higher than desirable level of inflammation regulators, whilst a high level of Omega 3 means higher levels of the anti-inflammatory ones. (we do need both but it is the ration that effects out sensitivity.)
A common denominator in obesity & diabetes (especially type II), is chronic inflammation of the cell membranes. This means that poor insulin sensitivity means you’ll gain fat, and that your ability to effectively partition nutrients will suffer.
Increasing your Omega 3 ratio is the easiest way to limit if not decrease inflammation and also improve your insulin sensitivity. Fish or Krill oil supplements, eating fatty deep sea fish and even supplementing with alpha-linolenic acid, an omega 3 fatty acid will all help.
Using olive, coconut or macadamia oils for cooking & dressings and cutting down as much as possible on ‘vegetable oils’ (seed oils really) like canola, safflower, peanut and blended oils will help also. All of these oils have a much higher level of Omega 6 than omega 3.
Now here is some concerning news – whereas fat tissue was once thought to be passive and largely inert, we now know that fat stores also have a function to control our whole body insulin sensitivity. Inflammatory responses in our body that cause insulin resistance & diabetes are in fact linked to our fat stores. The more of these you have the more likely it is that you will have insulin resistance and be at high risk of diabetes.
Fat it appears acts more as endocrine (hormone producing) organ, releasing hormone types called “adipokines.” It is these adipokines that control whole-body insulin sensitivity and inflammation. The famous hormone Leptin is an adipokine that is a strong nutrient partitioning agent that increases fat burning, decreases fat storage and improves insulin sensitivity.
Other adipokines work in the opposite direction. The way to influence which ones are produced is to up our Omega 3’s so the ‘good’ adipokines are released and the ‘bad’ ones are not..
Lastly – Don’t Stress!

This'll kill you - destress!!
Our insulin sensitivity falls off a cliff if we are under chronic, not acute stress. In these days of traffic jams, deadlines, taxes, poor economies etc etc it is hard to avoid experiencing at least some form of chronic stress.
Unchecked. Constant stress is a killer. It affects a plethora of body systems and erodes your health in numerous ways.
Learn to get enough sleep, exercise hard & regularly, enjoy regular sex, relax, do some meditating, choose who you spend time with and work at not worrying about the things outside of your control.
You’ll live longer, be happier and have much better insulin sensitivity…
See you next week – don’t forget to Tweet or face Book us!!
References
Kahn BB. Lilly lecture 1995. Glucose transport: pivotal step in insulin action. Diabetes 1996;45:1644-54.
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006;444:840-6.
SchutzY. Concept of fat balance in human obesity revisited with particular reference to de novo lipogenesis. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004;28 Suppl 4:S3-S11.
Schwarz JM, Linfoot P, Dare D, Aghajanian K. Hepatic de novo lipogenesis in normoinsulinemic and hyperinsulinemic subjects consuming high-fat, low-carbohydrate and low-fat, high-carbohydrate isoenergetic diets. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2003;77:43-50.
Parks EJ. Dietary carbohydrate’s effects on lipogenesis and the relationship of lipogenesis to blood insulin and glucose concentrations. Br J Nutr 2002;87 Suppl 2:S247-S253.
KoltermanOG, Greenfield M, Reaven GM, Saekow M, Olefsky JM. Effect of a high carbohydrate diet on insulin binding to adipocytes and on insulin action in vivo in man. Diabetes 1979;28:731-6.
Roberts R, Bickerton AS, Fielding BA, Blaak EE, Wagenmakers AJ, Chong MF, et al. Reduced oxidation of dietary fat after a short term high-carbohydrate diet. Am J Clin Nutr 2008;87:824-31.
SemenkovichCF. Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis.J Clin Invest 2006;116:1813-22.
Calder PC. n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and inflammatory diseases. Am J Clin Nutr 2006;83:1505S-19S.
SerhanCN, Hong S, Gronert K, Colgan SP, Devchand PR, Mirick G, et al. Resolvins: a family of bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits initiated by aspirin treatment that counter proinflammation signals. J Exp Med 2002;196:1025-37.
Schwab JM, Chiang N, Arita M, Serhan CN. Resolvin E1 and protectin D1 activate inflammation-resolution programmes. Nature 2007;447:869-74.
SimopoulosAP. Importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids: evolutionary aspects. World Rev Nutr Diet 2003;92:1-22.
BurdgeGC. Metabolism of alpha-linolenic acid in humans. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2006;75:161-8.
DeFilippisAP, Sperling LS. Understanding omega-3’s. Am Heart J 2006;151:564-70.
WellenKE, Hotamisligil GS.Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest 2005;115:1111-9.
ShoelsonSE, Lee J, Goldfine AB. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2006;116:1793-801.
Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM. Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature 2006;444:847-53.
GnudiL, Tozzo E, Shepherd PR, Bliss JL, Kahn BB. High level overexpression of glucose transporter-4 driven by an adipose-specific promoter is maintained in transgenic mice on a high fat diet, but does not prevent impaired glucose tolerance. Endocrinology 1995;136:995-1002.
Abel ED, Peroni O, Kim JK, Kim YB, Boss O, Hadro E, et al. Adipose-selective targeting of the GLUT4 gene impairs insulin action in muscle and liver. Nature 2001;409:729-33.
TrayhurnP. Endocrine and signalling role of adipose tissue: new perspectives on fat. Acta Physiol Scand 2005;184:285-93.
Havel PJ. Update on adipocyte hormones: regulation of energy balance and carbohydrate/lipid metabolism. Diabetes 2004;53 Suppl 1:S143-S151.
Wall R, Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF, Stanton C. Fatty acids from fish: the anti-inflammatory potential of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. Nutr Rev 2010;68:280-9.
Murata M, Kaji H, Takahashi Y, Iida K, Mizuno I, Okimura Y, et al. Stimulation by eicosapentaenoic acids of leptin mRNA expression and its secretion in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000;270:343-8.
Perez-Matute P, Marti A, Martinez JA, Fernandez-Otero MP, Stanhope KL, Havel PJ, et al. Eicosapentaenoic fatty acid increases leptin secretion from primary cultured rat adipocytes: role of glucose metabolism. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2005;288:R1682-R1688.
ItohM, Suganami T, Satoh N, Tanimoto-Koyama K, Yuan X, Tanaka M, et al. Increased adiponectin secretion by highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid in rodent models of obesity and human obese subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2007;27:1918-25.
Oh DY, Talukdar S, Bae EJ, Imamura T, Morinaga H, Fan W, et al. GPR120 is an omega-3 fatty acid receptor mediating potent anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects. Cell 2010;142:687-98.
KreierF, Fliers E, Voshol PJ, Van Eden CG, Havekes LM, Kalsbeek A, et al. Selective parasympathetic innervation of subcutaneous and intra-abdominal fat–functional implications. J Clin Invest 2002;110:1243-50.
RobidouxJ, Martin TL, Collins S. Beta-adrenergic receptors and regulation of energy expenditure: a family affair. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2004;44:297-323.
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D, Jr., Seeley RJ, Baskin DG. Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 2000;404:661-71.
Drawn in part from an excellent article on www.t-nation.com by Bill Willis PhDc and John Meadows, CSCS, CISSN – 9/14/2011
 and vegetables (frozen too!!) are high in fibre, create a higher TEF (Thermic Effect of Food – ie our body burns calories just to process them!) and have vitamins & minerals. These are the real deal – most are low in calorie count and high in nutrients and frankly I believe that you should eat as much low or unprocessed carbs as you want to. The only caveat being that you should ensure that you eat a variety of carbs,. If all you eat is pears – you could put on body fat due to the way fructose is metabolised – fibre or not. But a variety of fruit & vege choices ensure that this type of potential effect doesn’t happen.
and vegetables (frozen too!!) are high in fibre, create a higher TEF (Thermic Effect of Food – ie our body burns calories just to process them!) and have vitamins & minerals. These are the real deal – most are low in calorie count and high in nutrients and frankly I believe that you should eat as much low or unprocessed carbs as you want to. The only caveat being that you should ensure that you eat a variety of carbs,. If all you eat is pears – you could put on body fat due to the way fructose is metabolised – fibre or not. But a variety of fruit & vege choices ensure that this type of potential effect doesn’t happen.