HI & Welocme back!!
Today we’ll take a quick look at other factors that affect your RMR.
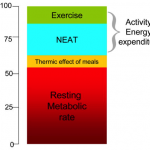
Your RMR isn’t just affected by your TEA & TEF (Thermic Effect of Activity & Thermic Effect of Food) – there are a large number of factors that often work in combination.
Some of these are:
- Body size – Because of their size adult bodies have more metabolic active tissue and a

higher RMR than a child. This does not hold true for obese folk as they have a lower RMR in general than lean folk. So to raise your RMR – get leaner
- Age – Our metabolism slows with age, due to loss muscle tissue along with hormonal and neurological changes. Not a lot we can do about getting older but keep an eye out for the ‘Counterclockwise’ program (coming later in 2011) which is a 100 day program aimed at reducing your biological markers of age.
- Growth – Babies, infants, children and teenagers all have a much higher energy demand per unit of body weight than adults. This is due to the energy demands of growth, the energy needed to maintain their body temperature when little, and the fact that (apart perhaps from teenagers) they are so physically active.
- Gender – In general – men have faster metabolisms than women because they tend to be larger, have more muscle tissue and have proportionately less body fat.
- Genetic predisposition – Your metabolic rate can also be partly decided by your genes.
- Amount of lean muscle tissue – Muscle burns more calories than fat – even at rest. The higher your proportion of muscle tissue to fat the better for your metabolism.
- Amount of body fat – Fat cells are metabolically less active than muscle cells (and most other tissues in your body) and burn far fewer calories. It’s simple: the more fat you have the slower your metabolism.
- Hormonal and nervous systems – Your RMR is controlled by the nervous and hormonal systems; and any hormonal imbalances (Insulin resistance, or increased Cortisol due to excessive stress, decreased Leptin or raised Ghrelin for example) influences how quickly or slowly your body burns calories / kilojoules. You can affect your hormones through carb manipulation, other dietary ‘tricks’, sleep and exercise. – See the accompanying Lose 20 in 30 Hormone Primer
- Dietary deficiencies – If, for example, your diet is low in iodine this reduces thyroid function, which in turn slows your metabolism. (The Lose 20 in 30 Nutrition program makes it damn near impossible to be deficient!)

Environmental temperature – By cooling or heating our immediate environment we can increase out RMR by causing the body to work harder to maintain our normal body temperature. Being too hot or too cold both burns calories / kilojoules.
- Infection or illness – In most cases our RMR increases when we are ill because our body has to work harder to build new tissues and to create an immune response. Not recommended for fat loss.
- Crash dieting, starving or fasting – Eating too few calories / kilojoules encourages our body to slow its metabolism to conserve energy; this means that your RMR can drop by up to 15 per cent if the change is sudden. Not recommended.
- Loss of lean weight due to sudden calorie restriction. This often happens when people go on a strict restricted calorie diet, forcing the body into what is known as “negative nitrogen balance.” This means that more protein is lost than is replaced through your diet and is a sign of more catabolism than is normal. This nitrogen imbalance causes a gradual loss in lean weight and lowers the RMR. On the upcoming Lose 20 in 30 program we avoid this by using a combination of calorie sparse, but nutrient dense foods – with a heavy emphasis on ingesting sufficient quantities of good protein along with an exercise regime that creates the need for your body to maintain its current muscle level if not increase it. This in turn forces your body to take more & more energy from your fat stores. (see the soon to be released Lose 20 in 30 Workout Program for details)
- Drugs – A number of drugs, legal, illegal, prescription and non-prescription can be used to increase your RMR. Caffeine is a good example of a legal drug that affects metabolism. Body builders used to use a ‘stack’ of caffeine, ephedrine and aspirin (in a specific ratio which I am NOT going to divulge) to really burn fat as well as some anti-asthma (no NOT Puffers) medications. These had obvious side-effects but they worked by amping up the RMR – something you can do but through effort not pill popping!!
Take Away: So if we manipulate our TEF & TEA wisely & strategically, we can increase our RMR and BMR which leads to a faster overall metabolism, a shift away from fat storage and a healthier, leaner body.
| Don’t foregt to Tweet or FB us!! |
Part seven next week….